Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C
Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C' title='Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C' />Expressions Microsoft Docs. An expression is a sequence of operators and operands. Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C' title='Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C' />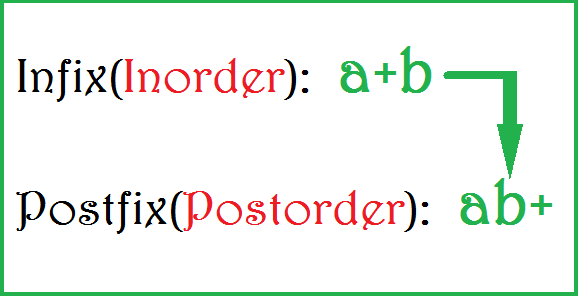 Morgan Stanley Columbia University Texas AM University Churchill College, Cambridge. C FAQ technical FAQ C11 FAQ publications WG21 papers. Some lab experiments must be performed using any circuit simulation software e. PSPICE. BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY Electrical Electronics Engineering. The Postfix notation is used to represent algebraic expressions. The expressions written in postfix form are evaluated faster compared to infix notation as. Explanation whiletokengetcharn Accepts Expression Character by Character Till Entered Character is n After Accepting Single Character do all. Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C' title='Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C' />
Morgan Stanley Columbia University Texas AM University Churchill College, Cambridge. C FAQ technical FAQ C11 FAQ publications WG21 papers. Some lab experiments must be performed using any circuit simulation software e. PSPICE. BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY Electrical Electronics Engineering. The Postfix notation is used to represent algebraic expressions. The expressions written in postfix form are evaluated faster compared to infix notation as. Explanation whiletokengetcharn Accepts Expression Character by Character Till Entered Character is n After Accepting Single Character do all. Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C' title='Program For Conversion Of Infix To Postfix Expression In C' /> In computer science, the shuntingyard algorithm is a method for parsing mathematical expressions specified in infix notation. It can produce either a postfix. This chapter defines the syntax, order of evaluation of operands and operators, and meaning of expressions. Expression classifications. An expression is classified as one of the following A value. Every value has an associated type. A variable. Every variable has an associated type, namely the declared type of the variable. A namespace. An expression with this classification can only appear as the left hand side of a memberaccess Member access. In any other context, an expression classified as a namespace causes a compile time error. A type. An expression with this classification can only appear as the left hand side of a memberaccess Member access, or as an operand for the as operator The as operator, the is operator The is operator, or the typeof operator The typeof operator. In any other context, an expression classified as a type causes a compile time error. A method group, which is a set of overloaded methods resulting from a member lookup Member lookup. A method group may have an associated instance expression and an associated type argument list. When an instance method is invoked, the result of evaluating the instance expression becomes the instance represented by this This access. A method group is permitted in an invocationexpression Invocation expressions, a delegatecreationexpression Delegate creation expressions and as the left hand side of an is operator, and can be implicitly converted to a compatible delegate type Method group conversions. In any other context, an expression classified as a method group causes a compile time error. A null literal. An expression with this classification can be implicitly converted to a reference type or nullable type. An anonymous function. An expression with this classification can be implicitly converted to a compatible delegate type or expression tree type. A property access. Every property access has an associated type, namely the type of the property. Furthermore, a property access may have an associated instance expression. When an accessor the get or set block of an instance property access is invoked, the result of evaluating the instance expression becomes the instance represented by this This access. An event access. Every event access has an associated type, namely the type of the event. Furthermore, an event access may have an associated instance expression. An event access may appear as the left hand operand of the and operators Event assignment. In any other context, an expression classified as an event access causes a compile time error. An indexer access. Every indexer access has an associated type, namely the element type of the indexer. Furthermore, an indexer access has an associated instance expression and an associated argument list. When an accessor the get or set block of an indexer access is invoked, the result of evaluating the instance expression becomes the instance represented by this This access, and the result of evaluating the argument list becomes the parameter list of the invocation. Nothing. This occurs when the expression is an invocation of a method with a return type of void. An expression classified as nothing is only valid in the context of a statementexpression Expression statements. The final result of an expression is never a namespace, type, method group, or event access. Rather, as noted above, these categories of expressions are intermediate constructs that are only permitted in certain contexts. A property access or indexer access is always reclassified as a value by performing an invocation of the get accessor or the set accessor. The particular accessor is determined by the context of the property or indexer access If the access is the target of an assignment, the set accessor is invoked to assign a new value Simple assignment. Otherwise, the get accessor is invoked to obtain the current value Values of expressions. Values of expressions. Most of the constructs that involve an expression ultimately require the expression to denote a value. In such cases, if the actual expression denotes a namespace, a type, a method group, or nothing, a compile time error occurs. However, if the expression denotes a property access, an indexer access, or a variable, the value of the property, indexer, or variable is implicitly substituted The value of a variable is simply the value currently stored in the storage location identified by the variable. A variable must be considered definitely assigned Definite assignment before its value can be obtained, or otherwise a compile time error occurs. Turbo C 4.5 For Windows 8 64 Bit Full Screen. The value of a property access expression is obtained by invoking the get accessor of the property. If the property has no get accessor, a compile time error occurs. Otherwise, a function member invocation Compile time checking of dynamic overload resolution is performed, and the result of the invocation becomes the value of the property access expression. The value of an indexer access expression is obtained by invoking the get accessor of the indexer. If the indexer has no get accessor, a compile time error occurs. Otherwise, a function member invocation Compile time checking of dynamic overload resolution is performed with the argument list associated with the indexer access expression, and the result of the invocation becomes the value of the indexer access expression. Static and Dynamic Binding. The process of determining the meaning of an operation based on the type or value of constituent expressions arguments, operands, receivers is often referred to as binding. For instance the meaning of a method call is determined based on the type of the receiver and arguments. The meaning of an operator is determined based on the type of its operands. In C the meaning of an operation is usually determined at compile time, based on the compile time type of its constituent expressions. Likewise, if an expression contains an error, the error is detected and reported by the compiler. This approach is known as static binding. However, if an expression is a dynamic expression i. The binding of such an operation is therefore deferred until the time where the operation is to be executed during the running of the program. This is referred to as dynamic binding. When an operation is dynamically bound, little or no checking is performed by the compiler. Instead if the run time binding fails, errors are reported as exceptions at run time. The following operations in C are subject to binding Member access e. MMethod invocation e. Me. 1,., e. NDelegate invocaton ee. NElement access ee. NObject creation new Ce. NOverloaded unary operators, true, false. Overloaded binary operators, lt lt, lt, lt Assignment operators, lt lt, Implicit and explicit conversions. When no dynamic expressions are involved, C defaults to static binding, which means that the compile time types of constituent expressions are used in the selection process. However, when one of the constituent expressions in the operations listed above is a dynamic expression, the operation is instead dynamically bound. Binding time. Static binding takes place at compile time, whereas dynamic binding takes place at run time.
In computer science, the shuntingyard algorithm is a method for parsing mathematical expressions specified in infix notation. It can produce either a postfix. This chapter defines the syntax, order of evaluation of operands and operators, and meaning of expressions. Expression classifications. An expression is classified as one of the following A value. Every value has an associated type. A variable. Every variable has an associated type, namely the declared type of the variable. A namespace. An expression with this classification can only appear as the left hand side of a memberaccess Member access. In any other context, an expression classified as a namespace causes a compile time error. A type. An expression with this classification can only appear as the left hand side of a memberaccess Member access, or as an operand for the as operator The as operator, the is operator The is operator, or the typeof operator The typeof operator. In any other context, an expression classified as a type causes a compile time error. A method group, which is a set of overloaded methods resulting from a member lookup Member lookup. A method group may have an associated instance expression and an associated type argument list. When an instance method is invoked, the result of evaluating the instance expression becomes the instance represented by this This access. A method group is permitted in an invocationexpression Invocation expressions, a delegatecreationexpression Delegate creation expressions and as the left hand side of an is operator, and can be implicitly converted to a compatible delegate type Method group conversions. In any other context, an expression classified as a method group causes a compile time error. A null literal. An expression with this classification can be implicitly converted to a reference type or nullable type. An anonymous function. An expression with this classification can be implicitly converted to a compatible delegate type or expression tree type. A property access. Every property access has an associated type, namely the type of the property. Furthermore, a property access may have an associated instance expression. When an accessor the get or set block of an instance property access is invoked, the result of evaluating the instance expression becomes the instance represented by this This access. An event access. Every event access has an associated type, namely the type of the event. Furthermore, an event access may have an associated instance expression. An event access may appear as the left hand operand of the and operators Event assignment. In any other context, an expression classified as an event access causes a compile time error. An indexer access. Every indexer access has an associated type, namely the element type of the indexer. Furthermore, an indexer access has an associated instance expression and an associated argument list. When an accessor the get or set block of an indexer access is invoked, the result of evaluating the instance expression becomes the instance represented by this This access, and the result of evaluating the argument list becomes the parameter list of the invocation. Nothing. This occurs when the expression is an invocation of a method with a return type of void. An expression classified as nothing is only valid in the context of a statementexpression Expression statements. The final result of an expression is never a namespace, type, method group, or event access. Rather, as noted above, these categories of expressions are intermediate constructs that are only permitted in certain contexts. A property access or indexer access is always reclassified as a value by performing an invocation of the get accessor or the set accessor. The particular accessor is determined by the context of the property or indexer access If the access is the target of an assignment, the set accessor is invoked to assign a new value Simple assignment. Otherwise, the get accessor is invoked to obtain the current value Values of expressions. Values of expressions. Most of the constructs that involve an expression ultimately require the expression to denote a value. In such cases, if the actual expression denotes a namespace, a type, a method group, or nothing, a compile time error occurs. However, if the expression denotes a property access, an indexer access, or a variable, the value of the property, indexer, or variable is implicitly substituted The value of a variable is simply the value currently stored in the storage location identified by the variable. A variable must be considered definitely assigned Definite assignment before its value can be obtained, or otherwise a compile time error occurs. Turbo C 4.5 For Windows 8 64 Bit Full Screen. The value of a property access expression is obtained by invoking the get accessor of the property. If the property has no get accessor, a compile time error occurs. Otherwise, a function member invocation Compile time checking of dynamic overload resolution is performed, and the result of the invocation becomes the value of the property access expression. The value of an indexer access expression is obtained by invoking the get accessor of the indexer. If the indexer has no get accessor, a compile time error occurs. Otherwise, a function member invocation Compile time checking of dynamic overload resolution is performed with the argument list associated with the indexer access expression, and the result of the invocation becomes the value of the indexer access expression. Static and Dynamic Binding. The process of determining the meaning of an operation based on the type or value of constituent expressions arguments, operands, receivers is often referred to as binding. For instance the meaning of a method call is determined based on the type of the receiver and arguments. The meaning of an operator is determined based on the type of its operands. In C the meaning of an operation is usually determined at compile time, based on the compile time type of its constituent expressions. Likewise, if an expression contains an error, the error is detected and reported by the compiler. This approach is known as static binding. However, if an expression is a dynamic expression i. The binding of such an operation is therefore deferred until the time where the operation is to be executed during the running of the program. This is referred to as dynamic binding. When an operation is dynamically bound, little or no checking is performed by the compiler. Instead if the run time binding fails, errors are reported as exceptions at run time. The following operations in C are subject to binding Member access e. MMethod invocation e. Me. 1,., e. NDelegate invocaton ee. NElement access ee. NObject creation new Ce. NOverloaded unary operators, true, false. Overloaded binary operators, lt lt, lt, lt Assignment operators, lt lt, Implicit and explicit conversions. When no dynamic expressions are involved, C defaults to static binding, which means that the compile time types of constituent expressions are used in the selection process. However, when one of the constituent expressions in the operations listed above is a dynamic expression, the operation is instead dynamically bound. Binding time. Static binding takes place at compile time, whereas dynamic binding takes place at run time.